Memory
- it is the foundational layer of computing where all data is stored
- data stored in memory is stored in bytes and by extension bits
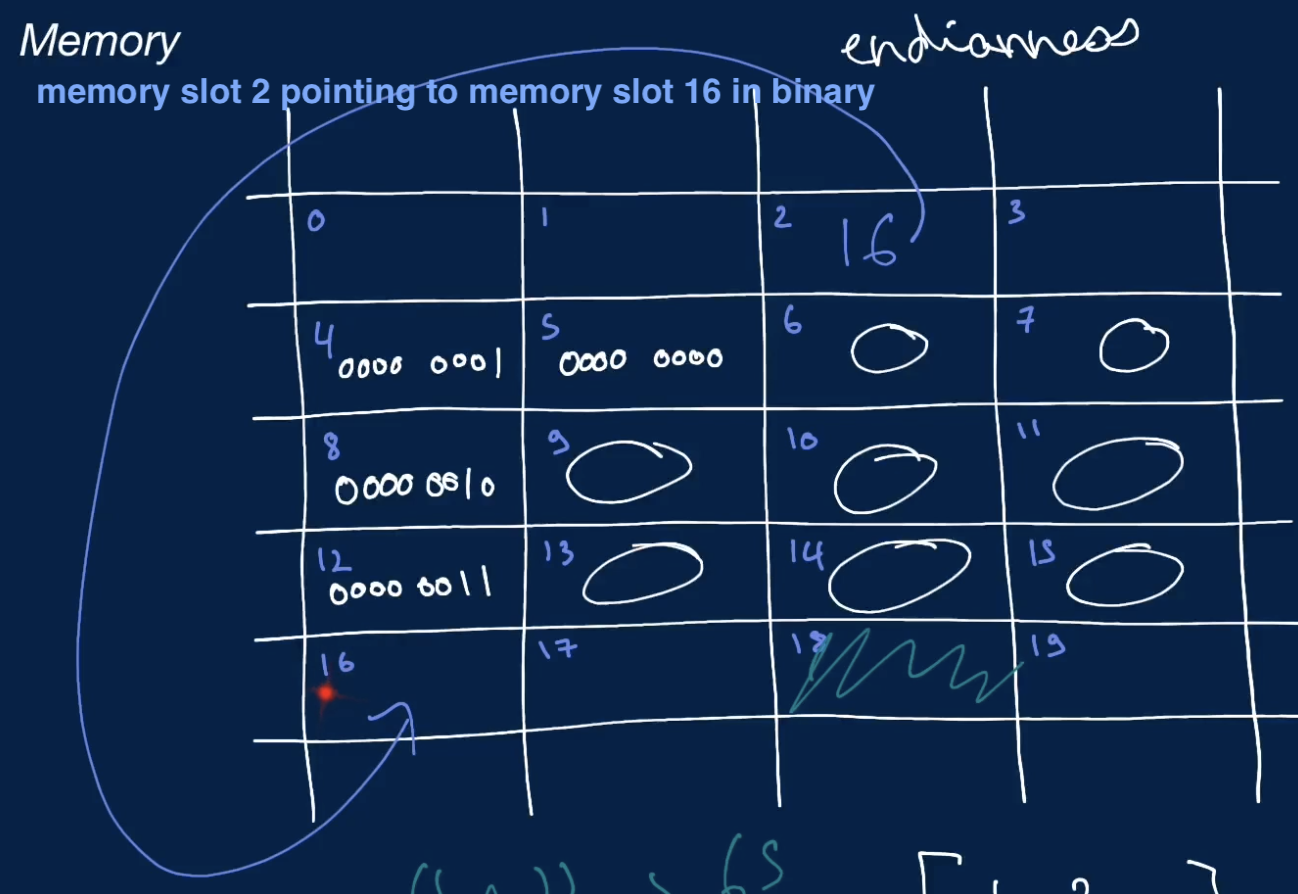
- bytes in memory can point to other bytes in memory
- so as to store references to other data
- the amount of memory that a machine has is bounded, making it valuable to limit how much memory an algorithm takes up
- accessing a byte or a fixed number of bytes (like 4 bytes or 8 bytes in the case of 32 bit and 64 bit integers) is an elementary operation which can be loosely treated as a single unit of operational work
- in other words
- memory is a bounded canvas of memory slots that can store data
- bounded means that you have a limited amount of data that you can store in it
- it is possible to run out of memory
- information that's stored in these memory slots are stored in base 2 format (binary number format) as bits
- 1 memory slot can hold 8 bits which is 1 byte
- when storing an integer in memory, that integer is a fixed-width integer
- meaning its either 32 bits or 64 bits
- if the Operating System (OS) using 32 bit architecture, it would always need 4 memory slot to hold 32 bits which is 4 bytes
- order is dependent of OS endianess
- Little endian
00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000- least significant bytes comes first
- Big endian
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000001- most significant bytes comes first
- Little endian
- when accessing a 32 bit integer, you will be accessing 4 memory slots
- this is a very inexpensive operation from a time point of view
- order is dependent of OS endianess
- if the Operating System (OS) using 32 bit architecture, it would always need 4 memory slot to hold 32 bits which is 4 bytes
- meaning its either 32 bits or 64 bits
- memory is a bounded canvas of memory slots that can store data
Example of memory usage
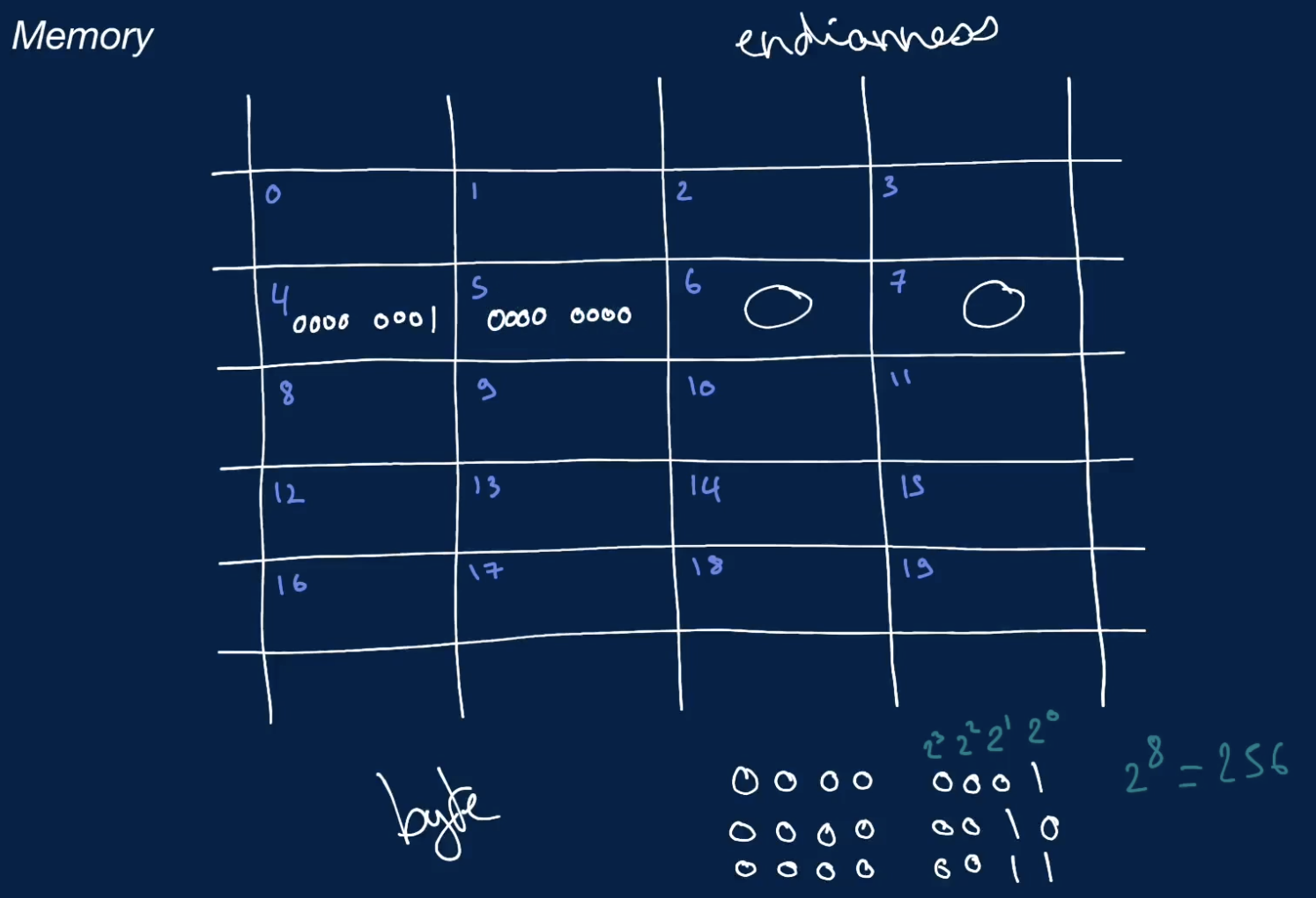
- e.g.: storing a fixed-width 32 bit integer value to a variable
foobar = 1- what happens under the hood is where the program is going to store this variable, the number 1 in a memory slot or series of memory slots that is free in the memory canvas
- if the value requires more than 1 memory slots to be stored, it will store them back to back
- e.g.: storing a list of fixed-width 32 bit integer value to a variable
foobar = [1, 2]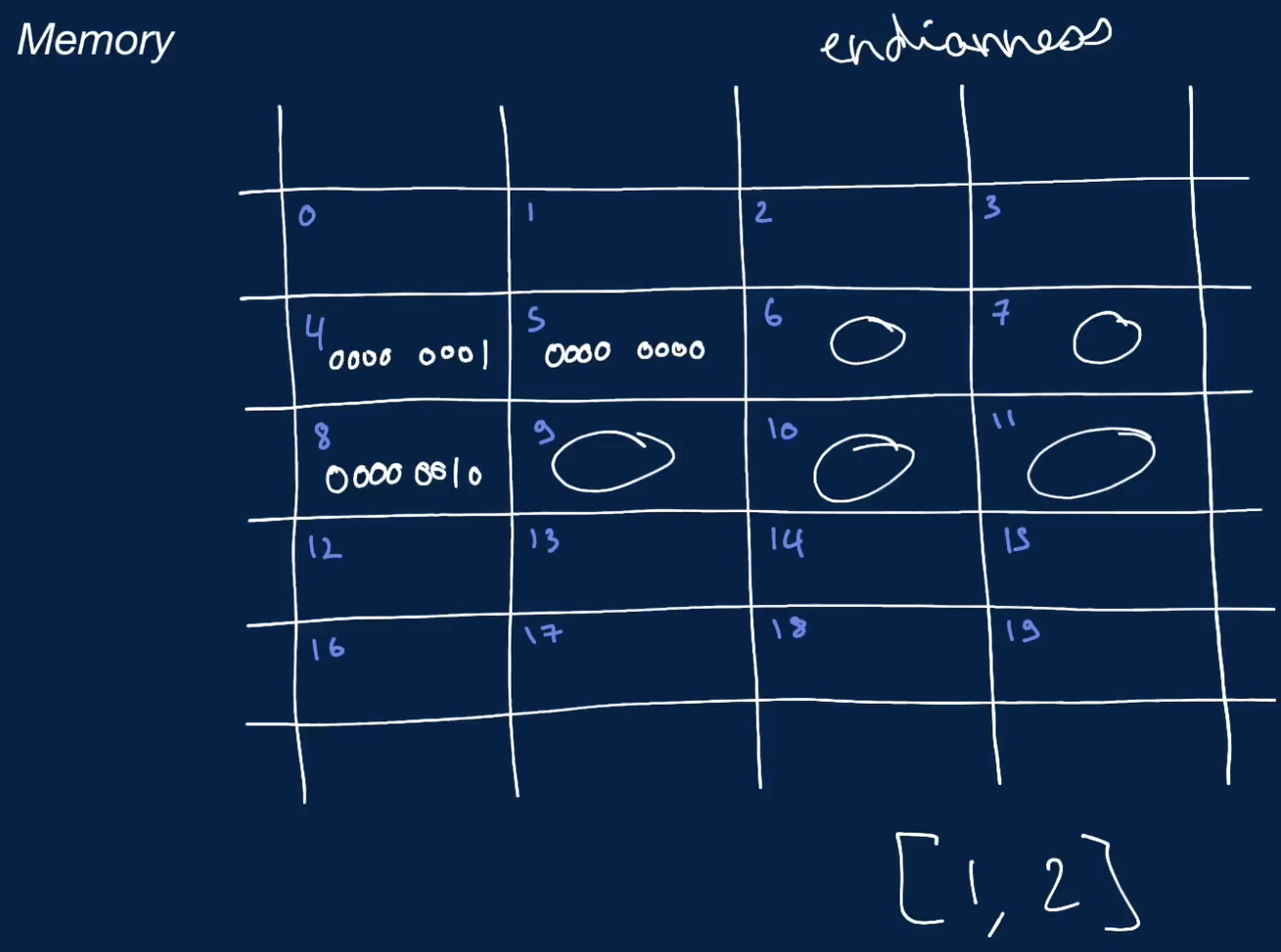
- the computer can access any of the memory slots very quickly with the memory address
Binary Digit (Bit)
- it is a fundamental unit of information in Computer Science that represents a state with 1 of 2 values
- usually 0 and 1
- any data stored in a computer is at the most basic level, represented in bits
Byte
- a group of 8 bits
- e.g.: 01101000 is a byte
- a single byte can represent up to 256 data values 2^8
- since a binary number is a number expressed with only 2 symbols, like 0 and 1
- a byte can represent all the numbers between 0 and 255 in binary format
1: 0000 0001
2: 0000 0010
3: 0000 0011
4: 0000 0100
- a byte can represent all the numbers between 0 and 255 in binary format
Fixed-Width Integer
- an integer represented by a fixed amount of bits
- e.g.: a 32 bit integer is a type int integer represented by 32 bits (4 bytes)
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000001- a 64 bit integer is a type long integer represented by 64 bits (8 bytes)
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000001
- a 64 bit integer is a type long integer represented by 64 bits (8 bytes)
- regardless of how large an integer is, its fixed-width-integer representation is by definition made up of a constant number of bits
- an operation performed on its fixed-width-integer representation consists of a constant number of bit manipulations
- since the integer is made up of a fixed number of bits
- an operation performed on its fixed-width-integer representation consists of a constant number of bit manipulations
American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII)
- map a character to a number
- e.g.: ASCII code for character "A" is 65 which would be turned into bits
- thus a string of characters will be stored as a list of numbers in memory
Pointers
- at any memory slot, a memory address of another memory slot can be stored in base 2 format (binary number format)
- allows you to not have to store specific data at a memory slot
- but instead point to another memory slot that stores that data
- e.g.: store memory slot 16 at memory slot 2