Flyweight design pattern
- It allows programs to support vast quantities of objects by keeping their memory consumption low
- it is achieved by sharing parts of object state between multiple objects
- thus allowing it to save RAM by caching the same data used by different objects
Structure
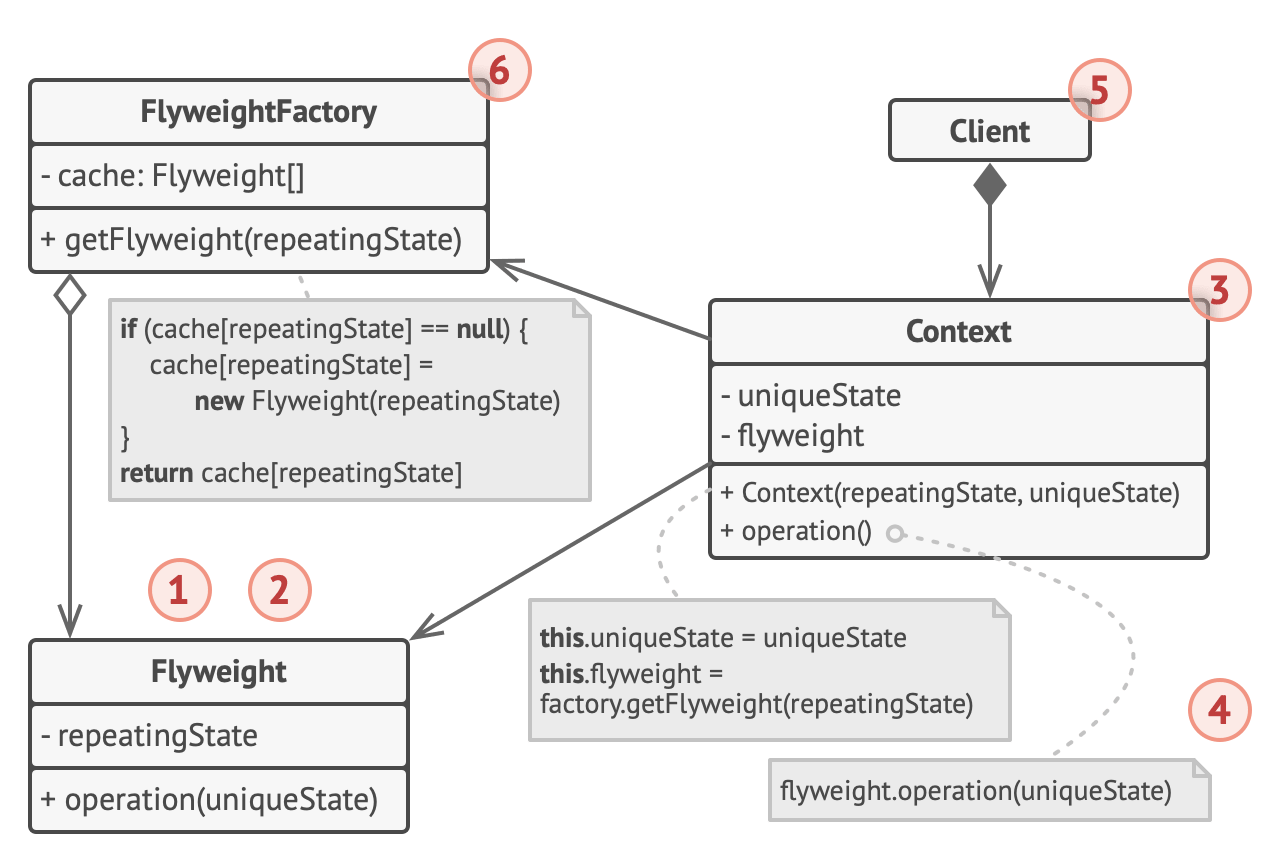
-
The Flyweight pattern is merely an optimization.
- Before applying it, make sure your program does have the RAM consumption problem related to having a massive number of similar objects in memory at the same time.
- Make sure that this problem can’t be solved in any other meaningful way.
-
The Flyweight class contains the portion of the original object’s state that can be shared between multiple objects.
- The same flyweight object can be used in many different contexts.
- The state stored inside a flyweight is called intrinsic.
- The state passed to the flyweight’s methods is called extrinsic.
-
The Context class contains the extrinsic state, unique across all original objects.
- When a context is paired with one of the flyweight objects, it represents the full state of the original object.
-
Usually, the behavior of the original object remains in the flyweight class.
- In this case, whoever calls a flyweight’s method must also pass appropriate bits of the extrinsic state into the method’s parameters.
- On the other hand, the behavior can be moved to the context class, which would use the linked flyweight merely as a data object.
-
The Client calculates or stores the extrinsic state of flyweights.
- From the client’s perspective, a flyweight is a template object which can be configured at runtime by passing some contextual data into parameters of its methods.
-
The Flyweight Factory manages a pool of existing flyweights.
- With the factory, clients don’t create flyweights directly.
- Instead, they call the factory, passing it bits of the intrinsic state of the desired flyweight.
- The factory looks over previously created flyweights and either returns an existing one that matches search criteria or creates a new one if nothing is found.
When to use
- it has a single purpose, which is to minimize memory intake
- thus it is not required if program doesn't struggle with a shortage of RAM