On this page
Spring it is an open source framework for building enterprise Java apps it aims to simplify the complex and cumbersome enterprise Java app development process by offering a framework that includes technologies such asAspect-oriented programming (AOP)Dependency Injection (DI)Plain Old Java Object (POJO) it is a lightweight framework that can be used to create scalable, secure, and robust enterprise web apps it can be considered as a collection of sub frameworks such asSpring Web Flow Spring MVC Spring ORM Spring also supports Kotlin and Groovyit is also the base that powers all other spring based projects such asSpring Boot Spring Cloud Spring GraphQL Core Features Inversion of Control (IoC) Container it is one of the core features of Spring that provides a streamlined way to configure and manage Java objects it is responsible for managing the lifecycle of a defined Java object, significantly increasing the configurability of a Spring-based application it uses the dependency injection or dependency lookup patterns to provide the object reference during runtime it consists of assembler code that is required for configuration management Spring provides org.springframework.beans and org.springframework.context packages that can be used to facilitate these functions Support for aspect oriented programming AOP aims to provide more modularity to the cross-cutting concerns, which are functions that span across the application, such asLogging Caching Transaction management Authentication AOP complements object-oriented programming by providing a different way to structure the program, where OOP modularity is based on classes In AOP, the main unit of modularity is an aspect (cross-cutting concern)This enables users to use AOP to create custom aspects and declarative enterprise services The IoC container does not depend on AOP, offering further freedom for developers to select their preferred programming method However, Aspect-Oriented Programming combined with the Spring IoC provides a robust middleware solution Data access framework Database communication issues are one of the common issues developers face when developing applications Spring simplifies the database communication process by providing direct support for popular data access frameworks in Java, such asJDBC, Hibernate, Java Persistence API (JPA) it offers features such as resource management, exception handling, and resource wrapping for all the supported data access frameworks, further simplifying the development process Transaction management framework Unlike the Java Transaction API (JTA), the Spring Transaction Management Framework is not limited to global and nested transactions Spring offers an abstraction mechanism for Java that enables users to:Work with local, global, and nested transactions Save points Simplify transaction management across the application The Spring Data Access Framework directly integrates with the Transaction Management Framework with support for messaging and cachingThis enables developers to create feature-rich transactional systems that span across the applications without depending on EJB or JTA Spring MVC framework The Spring MVC enables developers to create applications using the popular MVC pattern It is a request-based framework that allows developers to easily create customized MVC implementations that exactly suit their needs The core component of Spring MVC is the DispatcherServlet class which handles user requests and then forwards them to the correct controllerThis allows the controller to process the request, create the model and then provide the information to the end-user via a specified view Spring web service This Spring Web Service component provides a streamlined way to create and manage web service endpoints in the application It offers a layered approach that can be managed using XML and can be used to provide mapping for web requests to a specific object Spring test frameworks Spring simplifies testing within the framework with components likeMock objects TestContext framework Spring MVC Test Spring Framework Architecture Spring is built using different modules that enable different functionality
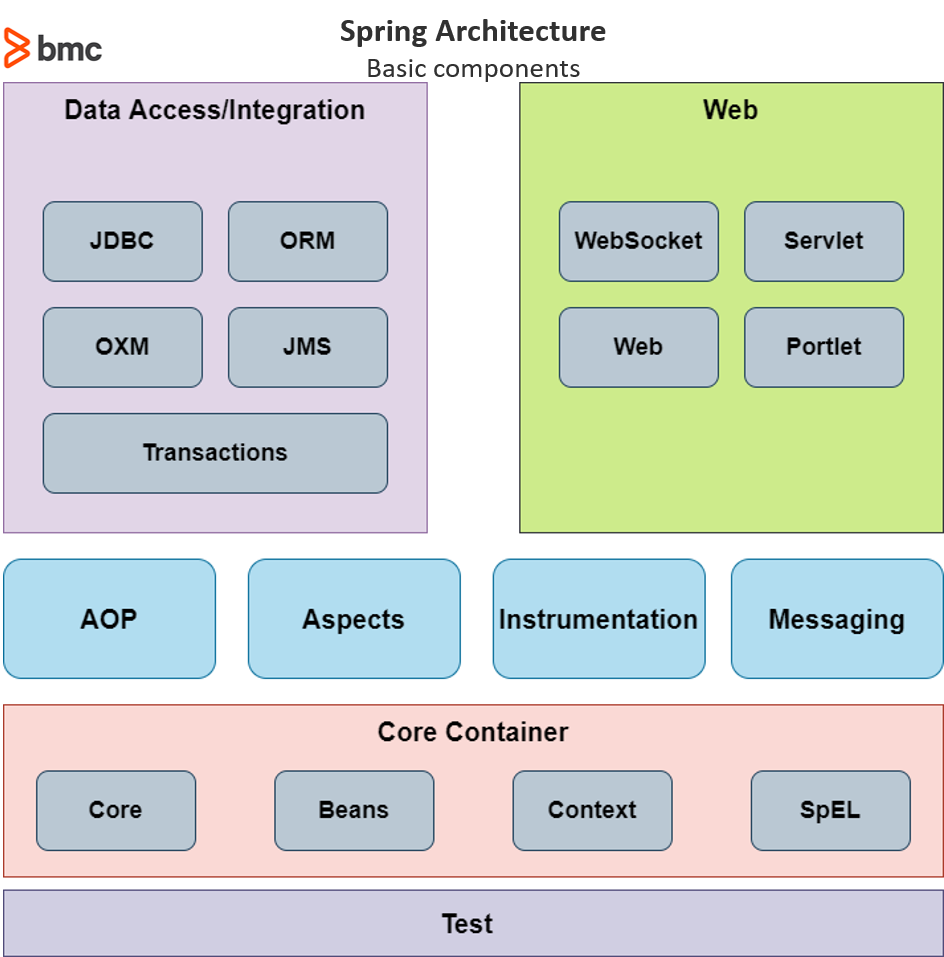
Core container This contains the fundamental modules that are the cornerstone of the Spring frameworkCore (spring-core) is the core of the framework that power features such as Inversion of Control and dependency injectionBeans (spring-beans) provides Beanfactory, which is a sophisticated implementation of the factory patternContext (spring-context) builds on Core and Beans and provides a medium to access defined objectsApplicationContext interface is the core part of the Context module, and the spring-context-support provides support for third-party interactions such as caching, mailing, and template enginesSpEL (spring-expression) enables users to use the Spring Expression Language to query and manipulate the object graph at runtime Data access/integration This includes the modules that are used to handle data access and transaction processing in an applicationJDBC (spring-jdbc) provides a JDBC abstraction layer that eliminates the need to separate JDBC coding when dealing with databasesORM (spring-orm) are integration layers for popular object-relational mapping API such as JPA, JDO HibernateOXM (spring-oxm) is the abstraction layer that supports Object/XML mapping implementations like JAXB, XStreamJMS (spring-jms) is the Java Messaging Service module that creates and consumes messages that directly integrate with the Spring messaging moduleTransaction (spring-tx) offers programmatic and declarative transaction management for classes that include special interfaces and POJOs Web The Web layer relates to modules that power web-based functions in SpringWebSocket (spring-websocket) powers the web socket-based communication for clients and serversServlet (spring-webmvc) is the Spring WebMVC module that contains the MVC and REST implementationsWeb (spring-web) provides all the basic web-oriented features and contains an HTTP client and web-related parts of the Spring remotingPortlet (spring-webmvc-portlet) provides the MVC implementation to be used in a portlet environment Other Modules AOP (spring-aop) provides an aspect-oriented programming implementation that can be used when creating applicationsAspects (spring-aspects) enables direct integration with the AspectJ programming extension by the eclipse foundationInstrumentation (spring-instrument) is the class instrumentation support and class loader implementations for application serversMessaging (spring-messaging) provides a robust platform to manage messaging in applicationsTest (spring-test) is the Spring test module that supports unit and integration testing with JUnit and TestNG