UML (Unified Modeling Language)
it is a general-purpose, developmental, modeling language in the field of software engineering that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system
before writing code, we need to design our computer system
- when working with a team, information needs to be shared
- need to have some plan or representation of the system
- when working with a team, information needs to be shared
UML is for describing system components and their interrelationships
it gives us a list of terms, abstractions, concepts and tools for high level modeling of the system
it is to some extent a design patterns in the programming world
the rules of UML is not limited to programming
- it is also used for modeling business processes, system design, drawing up organization, etc.
for visualizing your classes
example: class diagrams
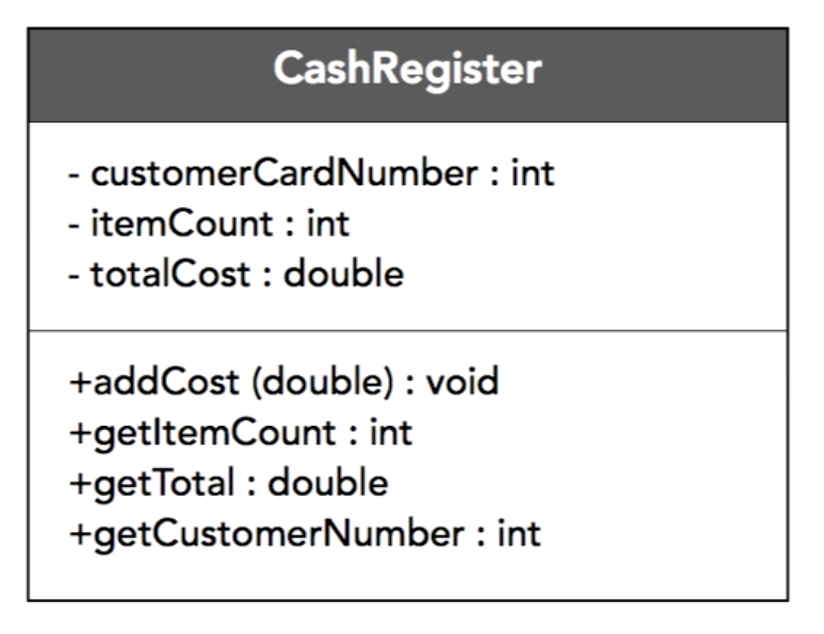
- top is the class name
- middle is the list of properties
- bottom is the methods the class has
Access modifiers
+public-private#protected
Formats
underlined textstatic fields or methodsALL_CAPSconstant fields or finalitalicabstract methodsexample: UML relations
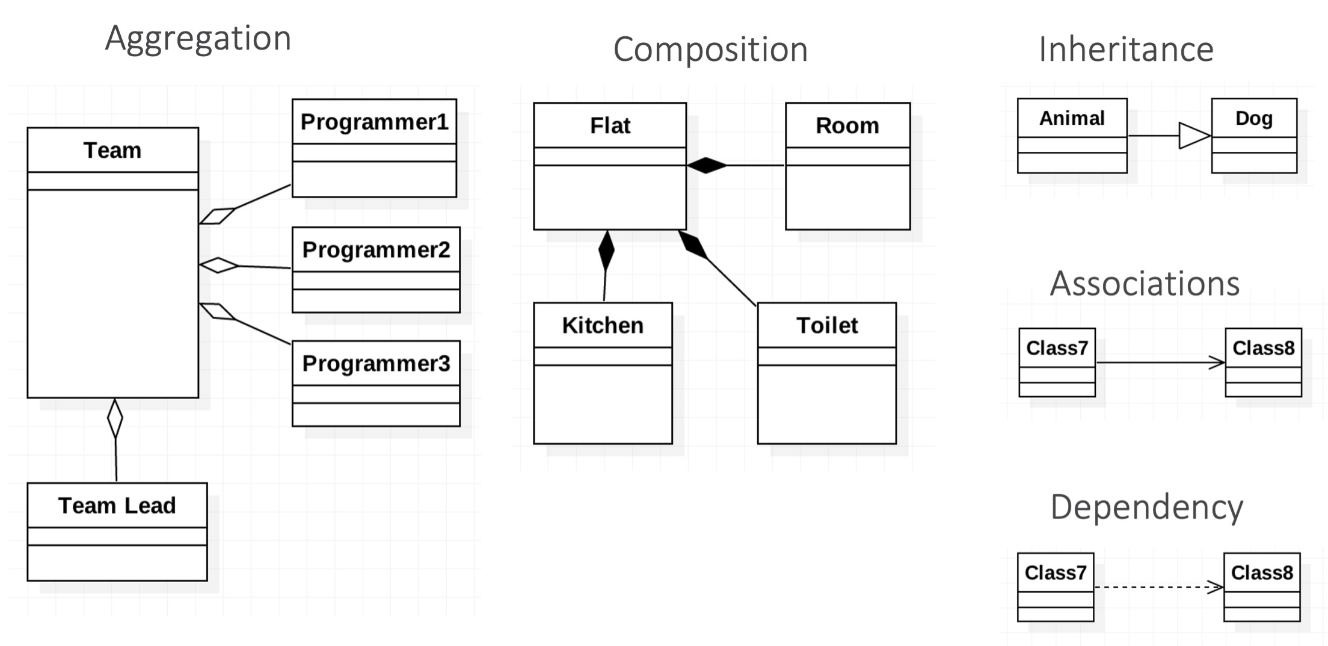
example: UML relationship

Association
Once classes and attributes have been identified and placed into a diagram, the next stage is to add
Associations- Usually, the system is not limited to just one class, there are tens, hundreds of classes, or even more
- Naturally, all these classes somehow interact with each other, somehow communicate, send messages to each other, call each other's methods, send events, and so on
- So the next step after creating those classes should be the visual representation of the relationship between these classes
There are different types of relationship between two classes / objects
The most basic type of relationship is
association- which means that the two classes are somehow related to each other
- we do not yet know exactly how this relationship is expressed and are going to clarify it in the future
This usually happens in the early stages of system design, when we know that there is a relationship
- but what specific relationship - inheritance, composition, or something else is not yet clear
When designing the system more globally
- The association helps when we indicate that 1 class in some way interact with another class
- At the initial stage, this is enough
An association is a relationship in which objects of one type are somehow related to objects of another type
- i.e. an object of 1 type contains or somehow uses an object of another type
- The player plays in a team
- We do not yet know what kind of relationship they have, or we are not interested in it at this stage of the design
- But we know that there is a relationship
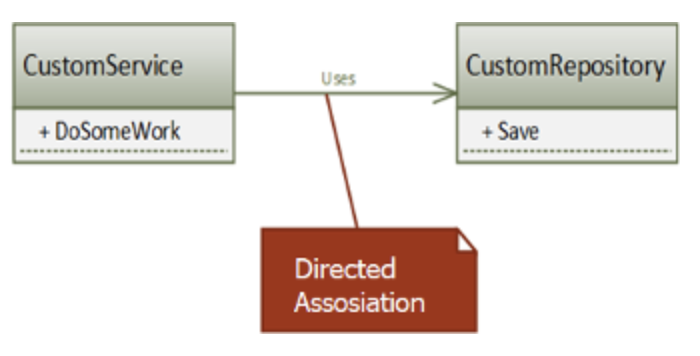
directional associationthe arrow shows us that we have a component that uses another component
In this case the CustomService uses the CustomRepository component, and not vice versa
example: Directed association
Inheritance
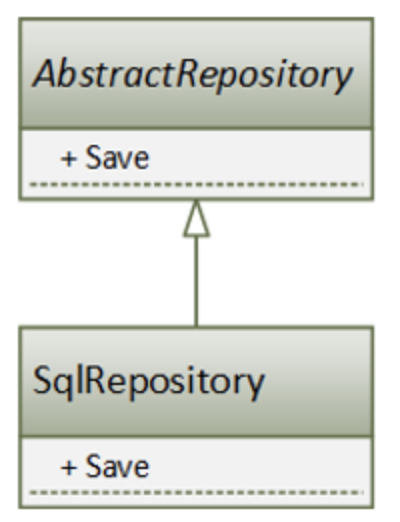
A more precise type of relationship is the public inheritance relationship (
IS A Relationship)- which says that everything that is true for the base class is true for its successor
With its help we can
- get polymorphic behavior
- abstract from the concrete implementation of classes
- deal only with abstractions (interfaces or base classes)
- do not pay attention to implementation details
Although inheritance is a great tool in the hands of any OOP programmer
- it is clearly not enough for solving all types of problems
- Firstly, not all relationships between classes are defined by the "is a" relationship
- secondly, inheritance is the strongest relationship between 2 classes that cannot be broken at runtime
- this relationship is static and, in strongly typed languages, is determined at compile time
in JavaScript, it has prototypal inheritance and can be changed for inherited classes
- properties can be changed by just changing prototypes
- But this is more an exception rather than a rule
- Because you cannot do this in classical inheritance
- once inherited in the source code, at run time you will not break this connection and you will not change the base class
- That is why inheritance is the strongest relationship between objects
- That is why architects and system designers recommend using inheritance only when it is necessary
- Because you cannot do this in classical inheritance
there is the concept of
preferring composition over inheritance- this suggests that composition can be broken at run time
- and you can replace one object in the composition at runtime with another, change the behavior dynamically
- You cannot do this with the inheritance
Composition and Aggregation
When relationships between components go beyond inheritance
- relationships such as composition and aggregation come to our rescue
- They both model a
HAS-A Relationshipand are usually expressed in that the class of a whole contains the fields (or properties) of its constituent parts
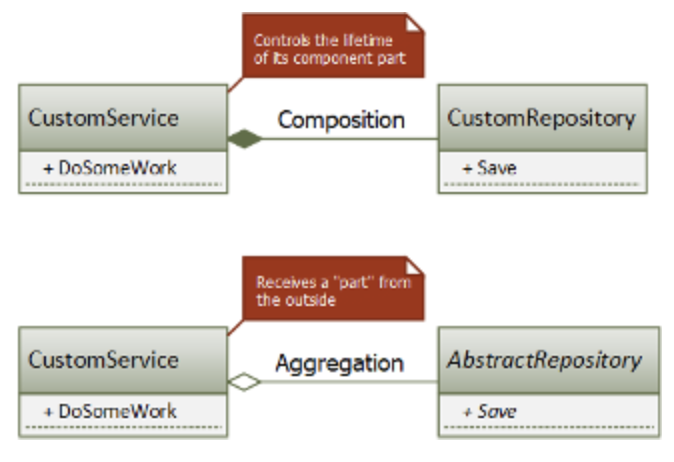
- the diamond is always on the side of the whole, and the simple line is on the side of the component
- a filled rhombus indicates a stronger bond - composition
- an open rhombus indicates a weaker bond - aggregation
- The difference between composition and aggregation
- composition: the whole explicitly controls the lifetime of its component part
- the part does not exist without the whole
- aggregation: although the whole contains its component part, their lifetimes are not related
- e.g.: the component part is passed via constructor parameters
- composition: the whole explicitly controls the lifetime of its component part
CompositeCustomServiceuses composition to manage its constituent partsAggregatedCustomServiceuses aggregation- explicit control of the lifetime usually leads to a higher coupling between the whole and the part
- since a specific type is used that closely connects the participants with each other
class CompositeCustomService {
// Composition
private readonly repository: CustomRepository = new CustomRepository();
public doSomething() {
// Usage of repository
}
}
class AggregatedCustomService {
// Aggregation
private readonly repository: AbstractRepository;
constructor(repository: AbstractRepository) {
this.repository = repository;
}
public doSomething() {
// Usage of repository
}
}
- Another example of composition
- Let us say a bicycle is a whole part and its components (shock absorbers, wheels, handlebars) are parts
- a single shock absorber without a bike makes no sense
- An example of aggregation
- Suppose there is a university or a school as a whole and teachers, professors as parts, for a certain period they may be part of this university, in some period they may not be included
- They can exist without this university after the university is destroyed, that is, its lifetime is over