Apache Maven
- standard definition
- a software project management and comprehension tool
- based on the concept of a Project Object Model (POM)
- Maven can manage a project's build, reporting and documentation from a central piece of information
- simple definition
- a project management tool with a POM
- a set of standards
- a project life cycle
- a dependency management system
- logic for executing plugin goals at lifecycle phases
- projects follow a consistent structure
- projects are IDE agnostic
- Maven allows for easy modifications to the project
- Maven simplifies the declaration of project dependencies
- it uses a POM file
Installation
- install with brew
brew install maven
- check maven version
mvn -version
Maven collector features
- dependency management
- ability to build lifecycle goals
- ability to run unit tests
Project Object Model (POM)
- it has a set of standards, a project lifecycle, a dependency management system, and logic for executing plugin at defined phases in a lifecycle
- projects are set up with default behaviors
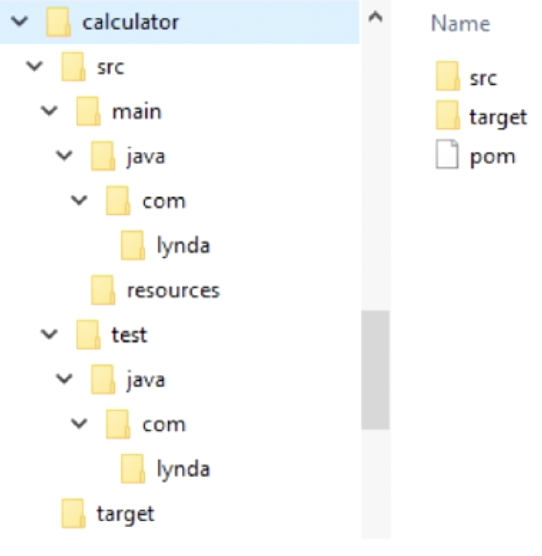
- source code must be in the
src/main/folder - resources necessary for the project are in another folder
- test cases are in a specifically name folder
target folderis used for the final JAR file
POM file
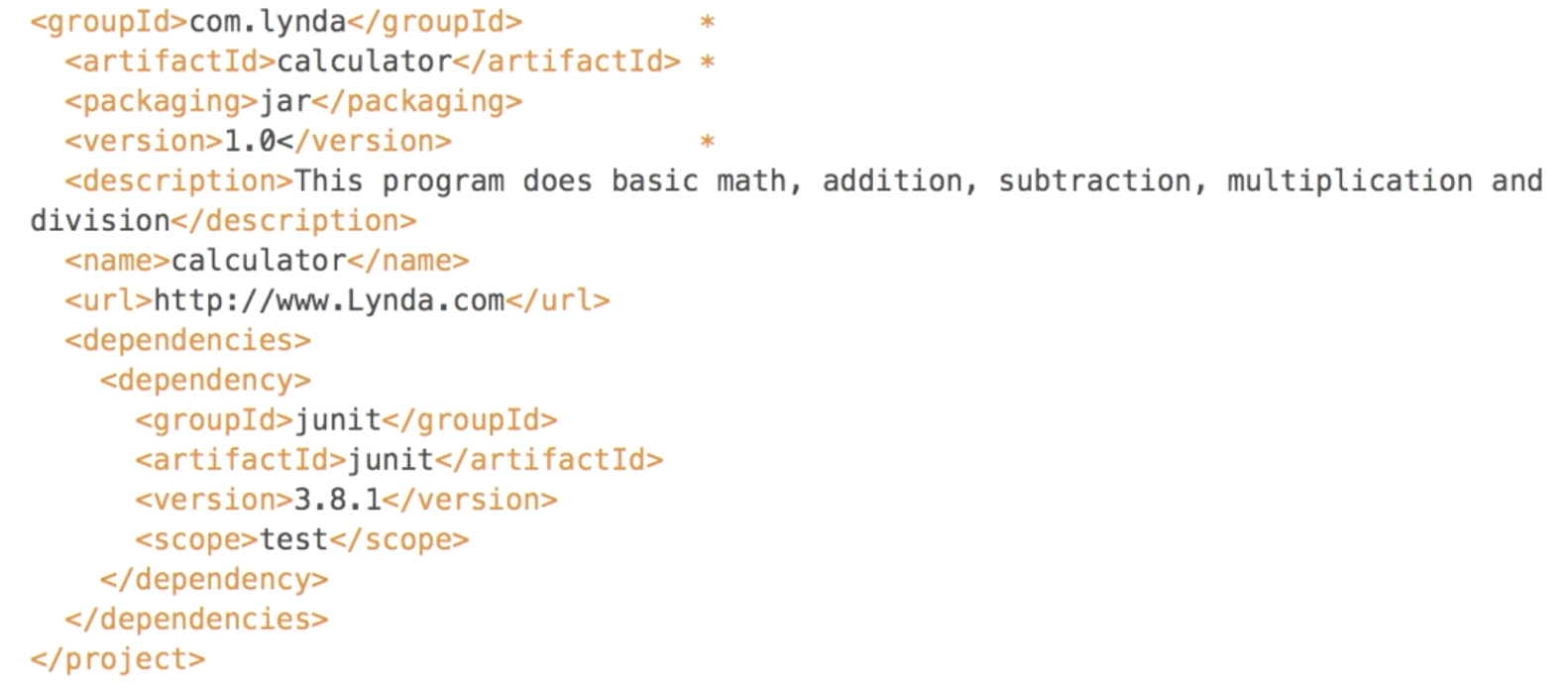
- must include
- project description
- unique set of
coordinates- highlighted by
*- groupId
- artifactId
- version
- highlighted by
- project attributes
- project's license
- project version
- program authors and contributors
- dependencies
- POM file can be separated into multiple POM files
POM Categories
- the POM contains all of the information about a project
- the file is stored with an XML extension
- minimum categories required
<project>
<groupId>com.projectname</groupId>
<artifactId>appname</artifactId>
<version>1.0</version>
</project> - common categories
- project coordinates
- project's license
- list of developers and contributors to the project
- list of project dependencies
- name of project
- url associated with project
- packaging type
- scope of element
- information about inheritance
buildcategory- add build related plugins
pluginManagementtag is optional, also work without it- it is normally used in a
parent POM
- it is normally used in a
<project>
...
<dependencies></dependencies>
<build>
<pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.0</version>
<configuration>
<target>8</target>
<source>8</source>
</configuration>
</plugin>
...
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
</build>
...
</project>reportingcategory- add reporting related plugins
<project>
...
<dependencies></dependencies>
<buid></build>
<reporting>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-report-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0</version>
</plugin>
...
</plugins>
</reporting>
...
</project>distributionManagementcategory is used for deploying<project>
...
<distributionManagement>
<repository>
<id>internal.repo</id>
<name>internal repository name</name>
<url>hot to repository</url
</repository>
</distributionManagement>
...
</project>servercategory is used to specify server definition- can also configure it in the
settings.xmlfield
<server>
<id>internal repo</id>
<username>someusername</username>
<password>somepassword</password>
</server>- can also configure it in the
POM syntax
- POM is documented in XML file
- file is stored in base directory
- syntax is similar to HTML file using
< >tags - every open XML tag must have a closing XML tag
- tags can be nested one inside the other
- XML declaration is optional
- all projects extend the super POM automatically
- sample
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.projectname</groupId>
<artifactId>appname</artifactId>
<version>1.0</version>
</project>
POM properties
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target>
<java.version>11</java.version>
<junit.version>5.2.0</junit.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>${junit.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
- purpose
- reduces duplication
- often times when configuration POM, tend to put the same value for an item and properties
- properties help to reduce this
- often times when configuration POM, tend to put the same value for an item and properties
- streamlines configuration
- often used in conjunction with a
parentPOM
- often used in conjunction with a
- helps keep items in sync
- such as versions of similar libraries
- properties allow you to leverage a version and reference it
- aids in upgrades
- can upgrade the property and it upgrades the rest for you
- reduces duplication
Parent POM
- a POM file that is stand-alone (no code associated with it)
- creates a list of dependency versions and plugins versions that the subordinate projects can leverage
- provides a way to control versions in 1 place so the subordinate projects don't have to specify the version, only the dependency
- it can provide properties and repositories
- a tool use to manage versions and licenses
- because can provide a pre-approved list of dependencies and artifacts
- a tool use to manage versions and licenses
- similar concept is a
Reactor- it builds on the concept of a parent POM
- used to build a group of related projects via the use of Parent POM
- Maven commands are executed on the parent, and reactor executes the commands on each module or artifact in the reactor
- the dependencies, if exists are handled in the correct order
- building reactor although not hard, it is time consuming
- structure example
root - pom
|_ module - POM
|_ module - POM
|_ module - POM- parent POM
<project>
...
<modules>
<module>module-name</module>
</modules>
...
</project> - child POM
<project>
...
<parent>
<groupId>com.projectname</groupId>
<artifactId>appname</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
...
</project>
- parent POM
features enabled by POM
- includes
- dependency management
- access to remote repositories
- universal reuse of build logic
- tool portability and integration
- allow IDEs to have a common place to find information about a project
- easy searching and filtering of project artifacts
Maven Life Cycles
- Default
- Clean
- Site
- each cycle has a few phases
- phases must be executed in order
- phrases are made up of goals
- Goals
- plugin goals are bound to phase of lifecycle
- goals can be triggered individually
- e.g.:
mvn dependency:analyze
- Goals
default life cycle phases
- main lifecycle
- Validate
- validate the project is correct
- Initialize
- Generate-sources
- Process-sources
- Generate-resources
- Process-resources
- Compile
- compile the source of the project
- Process-classes
- Generate-test-sources
- Process-test-sources
- Generate-test-resources
- Process-test-resources
- Test-compile
- Process-test-classes
- Test
- test the compiled source code using a unit testing framework
- Prepare-package
- Package
- package the compiled code
- Pre-integration-test
- Integration-test
- deploy the package into an environment where integration tests can be run
- Post-integration-test
- Verify
- run any checks to verify the package is valid
- Install
- install the package into the local repository
- Deploy
- copies the final package to the remote repository
- plugin goals can be attached to each lifecycle phase
- maven executes the goals attached to each phase
- each phase has 0 or more goals bound to it
- when you run
mvn install, multiple goals are executedtarget/folder with all the compiled code and jar file
- in the package phase, it executes the JAR goal
clean life cycle phases
- cleans project
- Pre-clean
- Clean
- Post-clean
site life cycle phases
- generates project documentation
- Pre-site
- site
- post-site
- site-deploy
Maven Repository
- central repository that contains open-source components
- Maven creates a local repository at
~/.m2location- foreign dependencies are installed here
- it also includes your JAR file and
pom.xmlfile for each install project - Maven repo search url address
Maven Dependency Management
- check dependencies
- dependencies could be used but not declared
- unused dependencies will be found
mvn dependency:analyze
- check dependencies tree
mvn dependency:tree
- allows for code reuse
- similar to using Java APIs
- most programmers have used the Math API
- dependencies are defined in the
pom.xmlfile<scope></scope>tag identifies what part of the life cycle the dependency is going to be used in- if scope tag is not included, it defaults to compile phase
- tests related must have the `
test - other scopes include
compile- the default scope
provided- used when JDK is expected to provide them
runtime- required for executing and testing, not compiling
test- not required during the normal operation of an app
system- similar to
provided - but must specify the explicit path to the JAR on the locals file system
- similar to
project dependencies
- Maven supports internal and external dependencies
- a common dependencies in Maven is
junit,log4j,jaxen - sample
<project ...>
...
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.14</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>jaxen</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxen</artifactId>
<version>1.1.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project> - using properties in parent POM example
<properties>
<log4j.version>1.2.14</log4j.version>
<junit.version>3.8.1</junit.version>
</properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>${log4j.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>${jaxen.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>- in child pom file example
- works fine if
enforcerplugin is not added
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>- verify with
mvn clean verify
- works fine if
- in child pom file example
project relationships
- Maven makes it easy to track down dependencies
- example of external relationships are
Log4jandJUnit - Internal is where project-a depends on project-b
- they are established using the Maven coordinates
- relationships are described as dependencies
- projects can inherit project relationships
transitive dependencies
- it is a dependency of a dependency
- provides a mechanism to only declare dependencies that you want
- thus you do not need to manage what dependencies is required from the dependencies that you need
- rules
- when 2 versions of the same artifact are needed
- the closest to the actual project wins
- e.g: actual project <- A needs package abc version 1.0 <- B needs package abc version 1.2
- package abc version 1.0 wins
- e.g: actual project <- A needs package abc version 1.0 <- B needs package abc version 1.2
- if
dependencyManagementtag is used- the chosen version will be used
- if declaring in local dependency
- local overrides all other transitive dependencies
- the closest to the actual project wins
- when 2 versions of the same artifact are needed
Best Practices
- grouping common dependencies
- can be done using multiple POM files
- allows other projects to reuse POM file
- choosing inheritance vs multi-module relationship
- multi-module: used when components are unrelated
- inheritance: used when projects share dependencies
- proper indentation for
pom.xmlfile - follow a standard layout where coordinates are listed first
Maven Plugins
- a plugin is a collection of 1 or more goals
- a goal is a unit of work in Maven
- can view goals of a plugin in the maven plugin website
Core plugins
- list of core plugins
- Compiler plugin
- contains goals for compiling source code and unit tests
- Surefire plugin
- used for executing unit tests and generating reports
- others
- clean, deploy, failsafe, install, resources, site, verifier
- Compiler plugin
- Maven also allows creating of custom plugins
- it can be written in multiple languages
- java, Groovy, Ruby, ...
- it can be written in multiple languages
- list of maven plugins url
- example of using a plugin and goal in the terminal
- plugin: compiler, goal: compile
mvn compiler:compile
- plugin: compiler, goal: compile
Packaging tools plugin
- list of packaging tools plugins
- JAR plugin
- creates JAR or Java Archive files
- others
- ear, ejb, rar, war, app-client/acr, shade, source, jlink, jmod
- JAR plugin
- example of using a plugin and goal in the terminal
- plugin: jar, goal: jar
mvn jar:jar
- plugin: jar, goal: jar
Reporting plugins
- list of reporting plugins
- changelog plugin
- changes plugin
- checkstyle plugin
- doap plugin
- docck plugin
- javadoc plugin
- jdeps plugin
- jxr plugin
- linkcheck plugin
- pmd plugin
- project-info-reports plugin
- surefire-report plugin
- example of using a plugin and goal in the terminal
- plugin: javadoc, goal: javadoc
- javadoc auto saves report in
target/site/apidocs/directory - launch the
index.htmlfile to view generated reportmvn javadoc:javadoc
- javadoc auto saves report in
- plugin: javadoc, goal: javadoc
Tools plugins
- list of tools plugins
- antrun, artifact, archetype, assembly, dependency, enforcer, gpg, help, invoker, jarsigner, jdeprscan, patch, pdf, plugin, release, remote-resources, scm, scm-publish, scripting, stage, toolchains, wrapper
- use help to find out more about a plugin
- example: archetype
mvn help:describe -DgroupId=org.apache.maven.plugins -DartifactId=maven-archetype-plugin
- example: archetype
Create a project with Maven
generate a new project with interactive mode
mvn archetype:generate -DarchetypeGroupId=org.apache.maven.archetypes -DarchetypeArtifactId=maven-archetype-quickstart
-DgroupId: defines where the project is located-DartifactId: app name, only use-to divide words-Dversion: can just use the default version-Dpackage: this should match with thegroupId
Sample program
mvn archetype:generate -DgroupId=com.projectname -DartifactId=appname -DarchetypeArtifactId=maven-archetype-quickstart -DInteractiveMode=false
- View the full pom file contents
- in the same directory where the
pom.xmlfile is located atmvn help:effective-pom
- in the same directory where the
- install the all dependencies and plugins
mvn install
- if a compilation error were to occur due to old version issue, add the following into the
pom.xmlfile, just above thedependenciestag<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>18</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>18</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
- if a compilation error were to occur due to old version issue, add the following into the
- run the app
- method 1
-cpflag is used for class search path- it will search directories and look for
zip/jarfiles
- it will search directories and look for
appname-1.0-SNAPSHOTis correct if default version is usedjava -cp target/appname-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar com.projectname.App
appname-0.0.1is correct if0.0.1version is setjava -cp target/appname-0.0.1.jar com.projectname.App
- method 2
- add
maven-jar-plugin<project>
...
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-jar-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0.2</version>
<configuration>
<archive>
<manifest>
<mainClass>com.domainname.appname.Main</mainClass>
</manifest>
</archive>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
...
</project>java -jar target/appname-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar
- add
- method 3
- add
exec-maven-plugin<project>
...
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.codehaus.mojo</groupId>
<artifactId>exec-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.5.0</version>
<configuration>
<mainClass>com.dockerapp.App</mainClass>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
...
</project>mvn clean package exec:java
- add
- method 4
- run with docker using maven
<project>
...
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-jar-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0.2</version>
<configuration>
<archive>
<manifest>
<mainClass>com.domainname.appname.Main</mainClass>
</manifest>
</archive>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>docker</id>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>io.fabric8</groupId>
<artifactId>docker-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>0.20.1</version>
<configuration>
<images>
<image>
<name>hellojava</name>
<build>
<from>openjdk:latest</from>
<assembly>
<descriptorRef>artifact</descriptorRef>
</assembly>
<cmd>java -jar maven/${project.name}-${project.version}.jar</cmd>
</build>
<run>
<wait>
<log>Hello World!</log>
</wait>
</run>
</image>
</images>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>docker:build</id>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>build</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
<execution>
<id>docker:start</id>
<phase>install</phase>
<goals>
<goal>run</goal>
<goal>logs</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</profile>
</profiles>
...
</project> - packaging
mvn package -Pdocker
- package and run
mvn install -Pdocker
- run with docker using maven
- method 1
Web app
mvn archetype:generate -DgroupId=com.projectname -DartifactId=webappname -DarchetypeArtifactId=maven-archetype-webapp -DInteractiveMode=false
Unit testing with Maven
- Maven provides built-in support for unit testing
- JUnit is used to test app
Test/directory is automatically created with a test app- run test
mvn test
Add resources folder
- add resources folder to add files for inputs
- can be
txtfiles - use
Scannerlibrary to read file inresourcesfolder
- can be
- for
mainfolder- create
resourcesfolder inmainfolder
- create
- for
testfolder- create
resourcesfolder intestfolder
- create
Packaging App
- packaging information is stored in
pom.xmlfile<packaging>jar</packaging> - default is
jarif the type is omitted - run package
- also works with
mvn install,mvn testmvn package
- add
cleanoptional command to remove issues with other Maven operationsmvn clean package
- add
siteoptional command to generatesurefiredocumentation for usmvn clean package site
- also works with