Availability
- when evaluating a system, 2 of the things you wanna think about are the system's latency and throughput
- there is also a 3rd thing to think about and that is
Availability
- there is also a 3rd thing to think about and that is
- in this day and age, most systems almost have an implied guarantee of availability
- availability is something that matters a lot both to end users of systems and to system designers
- it matters so much that for certain systems
- there isn't an implied but have an explicit guarantee of availability
- it matters so much that for certain systems
- many service providers have SLAs (Service-Level Agreement)
- Although high availability is very important, sometimes it might be undesired
- having high availability comes with trade-offs
- because it is difficult to achieve high availability
- it might come at other costs like higher latencies or lower throughput
- having high availability comes with trade-offs
- as a system designer, have to think whether a system or parts of the system should be highly available
- e.g.: in Stripe, their core services of handling payments and of charging customers is likely a highly available service
- while their dashboard that business can use to monitor their sales isn't as critical as the core payment service that Stripe provides therefore does not need as much availability compared to the core services
What is availability
System's Fault Tolerance
- how resistant a system is to failures
- e.g.: what happens if a server in the system fails
- what happens if the database fails
- is the system gonna completely go down or will be still be operational
- e.g.: what happens if a server in the system fails
Percentage of time
- the percentage of time in a given period (like a month or a year) are at least operational enough
- such that all of its primary functions are satisfied
How availability is measured
- it is measured as the percentage of a system's uptime in a given year
- e.g.: if a system is up and operational for half of an entire year
- then that system has 50% availability which is very bad
- e.g.: if a system is up and operational for half of an entire year
- when dealing with availability, usually we are dealing with very high percentages
- therefore we measure availability not exactly in percentages but rather in
Nines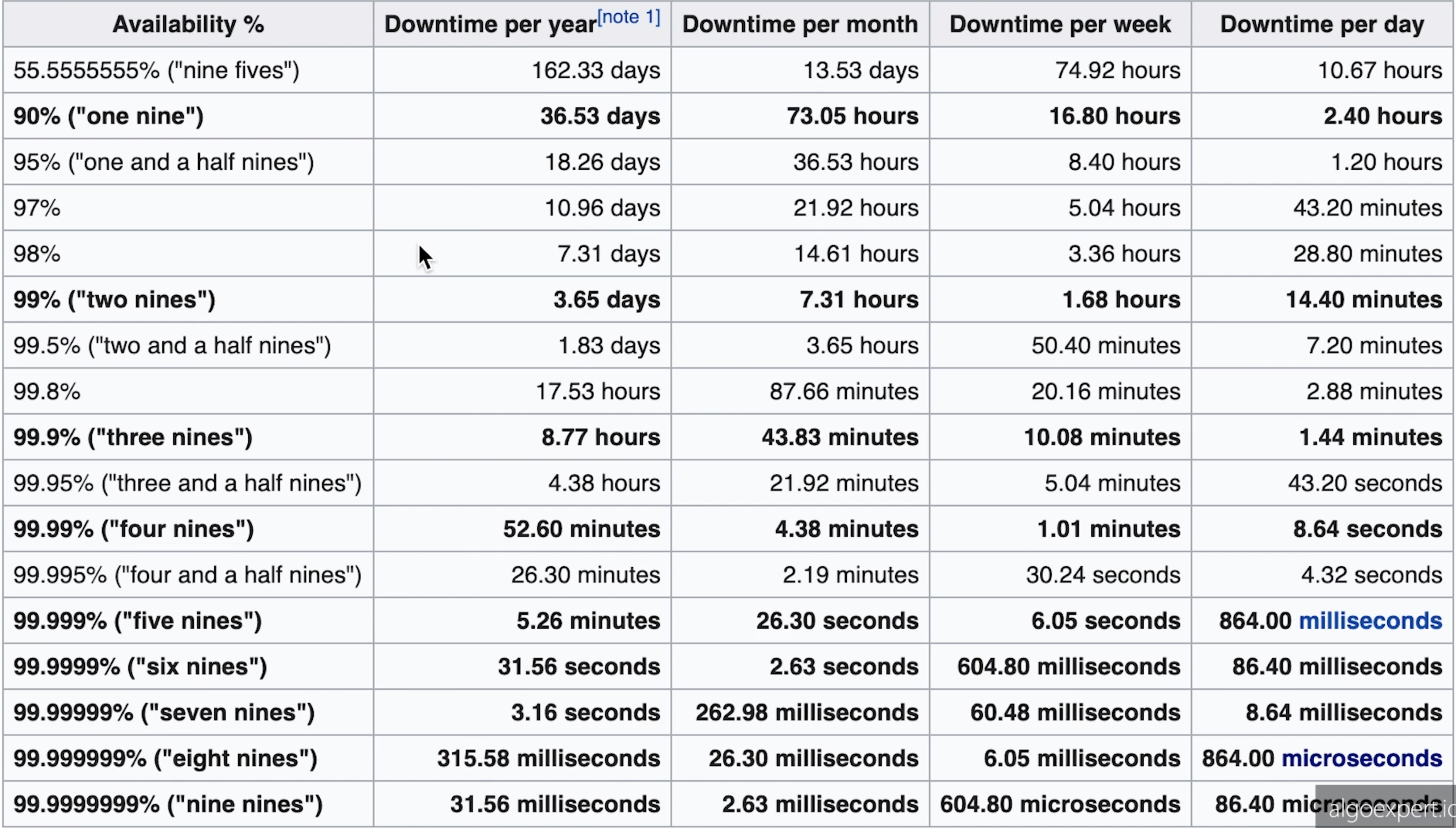
- a system with 5 nines and above are regarded as
highly availableorhigh availability
- a system with 5 nines and above are regarded as
- therefore we measure availability not exactly in percentages but rather in
How to improve the availability
- ensure that the system doesn't have single points of failure
- single places in the system that if they fail would cause the entire system to fail
- this can be solved with
redundancy
- need to have a rigorous processes in place to handle system failures
- because it is possible that system failures will require human intervention
- e.g.: if server crashes, need human to bring it back up
- with the processes in place, it will ensure that system failures fix happens in the proper time frame
- because it is possible that system failures will require human intervention
Terms used
Process
- a program that is currently running on a machine
- should always assume that any process may gt terminated at any time in a sufficiently large system
Server
- a machine or process that provides data or service for a client
- usually by listening for incoming network calls
- a single machine or piece of software can be both a client and a server at the same time
- e.g.: a single machine could act as a server for end users and as a client for a database
Node/Instance/Host
- these 3 terms refer to the same thing most of the time
- a virtual or physical machine on which the developer runs processes
- sometimes the word
serveralso refers to this same concept
Availability
- the odds of a particular server or service being up and running at any point in time
- usually measured in percentages
- a server that has 99% availability will be operational 99% of the time
- this would be described as having 2 nines of availability
High Availability
- used to describe systems that have particularly high levels of availability
- typically 5 nines or more
- sometimes abbreviated "HA"
- typically 5 nines or more
Nines
- typically refers to percentages of uptime with the number 9
- e.g.: 5 nines of availability means an uptime of 99.999% of the time
- below are the downtimes expected per year depending on those 9s:
- 99% (2 nines): 87.7 hours
- 99.9% (3 nines): 8.8 hours
- 99.99%: 52.6 minutes
- 99.999%: 5.3 minutes
Redundancy
- the process of replicating parts of a system in an effort to make it more reliable
Passive redundancy
- passive redundancy is when you have multiple components at a given layer in the system
- if at any point 1 of those components e.g. 1 of the servers or load balancers, dies
- nothing really gonna happen as the other components are still able to continue running smoothly
- they might have more load but will be fine until the broken component gets fixed
- nothing really gonna happen as the other components are still able to continue running smoothly
- normally used in airplane engines
- if at any point 1 of those components e.g. 1 of the servers or load balancers, dies
- e.g.:
- adding more servers if it is server issue
- adding more load balancers if if it is over loaded
Active redundancy
- it is when you have multiple machines that work together in such a way
- that only 1 or few of the machines are gonna be typically handling traffic or doing work
- if 1 of the ones that is handling traffic or doing work fails
- the other machines will know about it and will reconfigure themselves to take over the job of the dead machine
- this is also known as
leader election
- this is also known as
- the other machines will know about it and will reconfigure themselves to take over the job of the dead machine
SLA (Service-Level Agreement)
- is an agreement on the system's availability between service provider (the people behind the service or system that is being sold or provided) and the customers or end users of this service or of the system
- is a collection of guarantees given to a customer by a service provider
- it typically make guarantees on a system's availability through explicit written SLAs
- amongst other things, it is made up of 1 or multiple SLOs (Service-Level Objective)
- SLA e.g.: refer to Google Cloud Spanner SLA example
SLO (Service-Level Objective)
- is a guarantee given to a customer by a service provider
- it typically make guarantees on a system's availability
- e.g.: the percentage of uptime guarantee is an SLO
- amongst other things, SLOs is the components of an SLA (Service-Level Agreement)