On this page
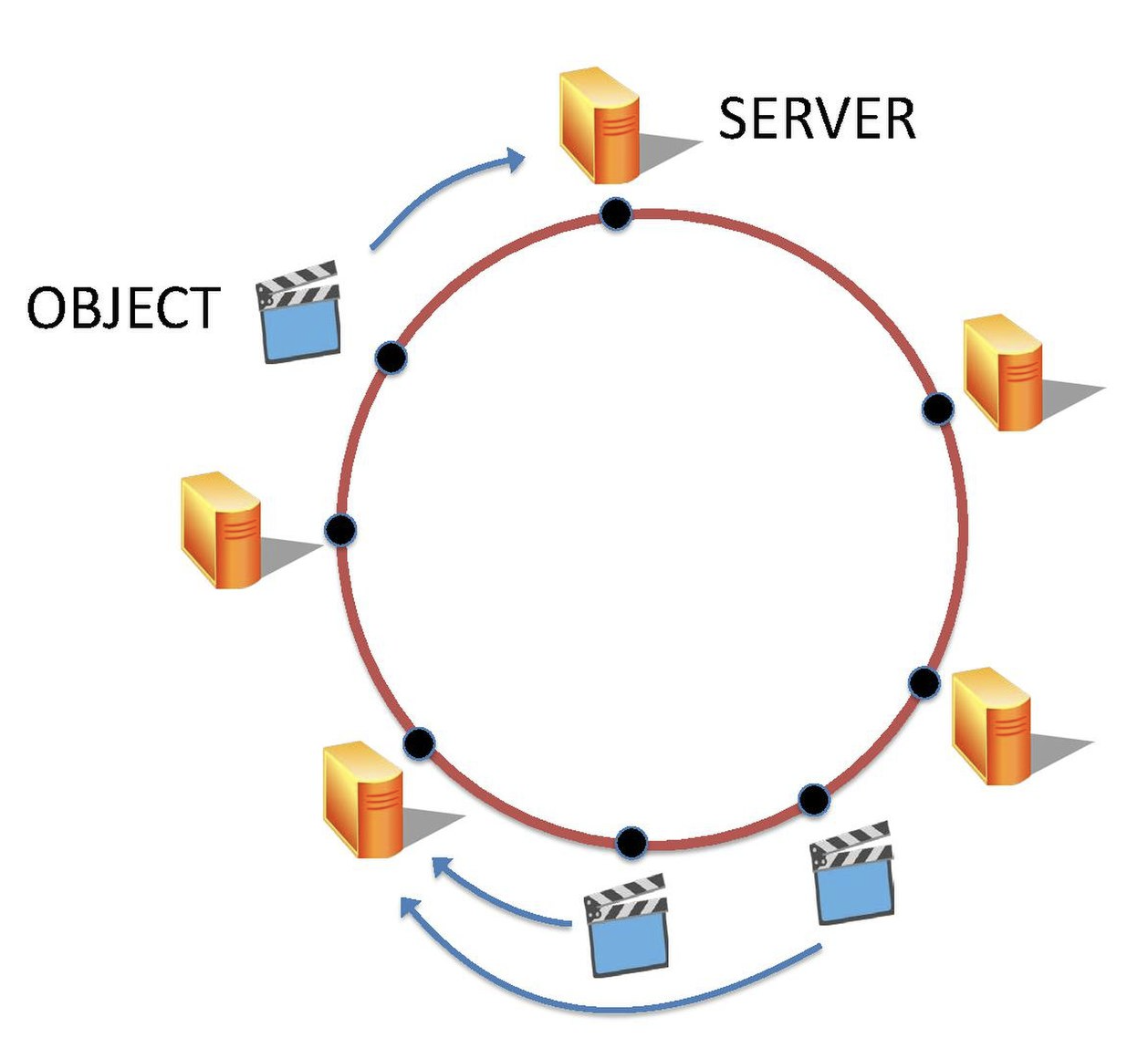
Hashing hashing is an action that you can perform to transform an arbitrary piece of data into a fixed size value (typically an integer value)in terms of system design, the arbitrary piece of data can be an IP address, username, or HTTP request, anything that can be hashed or transformed into an integer value potentional problem with round robin strategy approach of a load balancer a client performs a computional heavy request and cache is stored in server aif the same client performs the same heavy request but instead got redirected to a different server, the cache is gone and have to be cached again naive solution via hashing first hash the requests that comes into the load balancerthen based on the hash value, the request will be redirected to the server located at the hash value by doing so, all request made by the same client will always be redirected to the same server however, other problems can arise when dealing with large scale distributed systemse.g.: servers can die, or a server is overloaded and requires new servers in the case where a new server is added, or when a server failswe would need to modify the hashing logic to produce different hash values for the server locationshowever, by doing so, all the clients that were redirected to a specific server would change, causing the servers to compute the cache again therefore, this solution does not work the moment a server fails or a new server is added Better solution by using Consistent hashing or Rendezvous hashing Terms used Hashing function a funtion that takes in a specific data type (such as a string or an identifier) different inputs may have the same outputbut a good hashing function attempts to mnimize those hashing collisions (equivalent to maximizing uniformity) a good hashing function will evenly distribute your data values in practice you never write your own hashing functionnormally use a pre-made industry grade hashing function or hashing algorithm Consistent hashing a type of hashing that minimizes the number of keys that need to be remapped when a hash table gets resized it's often used by load balancers to distribute traffic to servers it minimizes the number of requests that get forwarded to different servers when new servers are added or when existing servers are brought down if a server gets removed or is newly added, most of the clients will still be redirected to the same server the same server can also be placed at multiple locations to allow more clients to be redirected to it
Rendezvous hashing a type of hashing also coined highest random weight hashing allows for minimal re-distribution of mappings when a server goes down for every client, it will calculate a score or ranks the servers or destinationsthe client would then be associated with the highest score or ranking of the server in the event a server fails, a new calculation of the highest score or ranking of the server will be done and thus be associated to the new server SHA (Secure Hash Algorithms) is a collection of cryptographic hash functions used in the industry SHA-3 is a popular choice to use in a system these days