Two Pointers: Same Direction
Middle Of Linked List
Find the middle node of a linked list.
Input: 0 1 2 3 4
Output: 2
If the number of nodes is even, then return the second middle node.
Input: 0 1 2 3 4 5
Output: 3
class Node {
constructor(val, next = null) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
function middleOfLinkedList(nodes) {
let slow = nodes;
let fast = nodes;
while (fast && fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow.val;
}
Explanation
- If it was an array, then we can get its length and middle element trivially
- For a linked list, we have to traverse it to find its length l
- We can find l by traversing the list once and then find the middle element by traversing it again and stop on the l/2th element
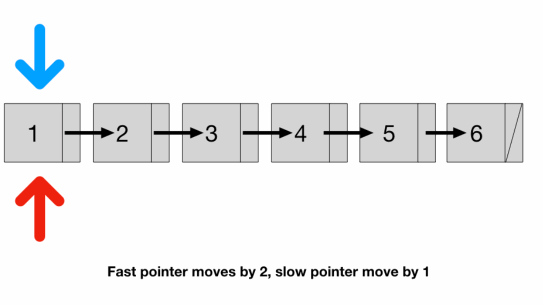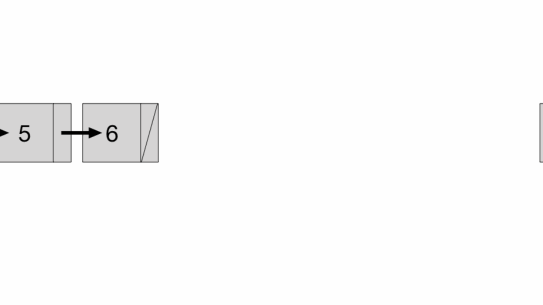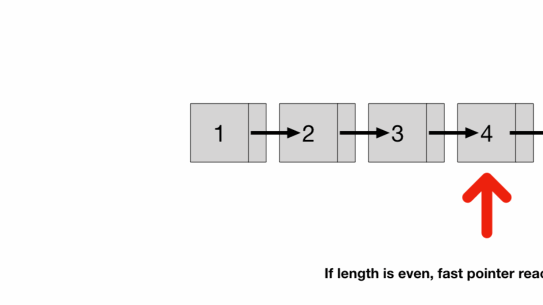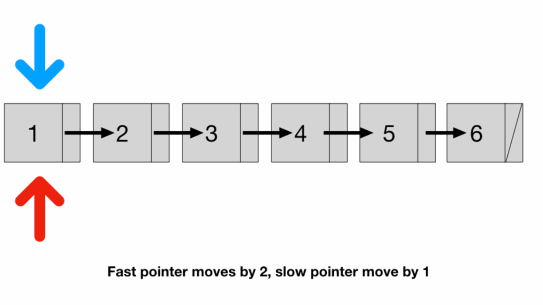
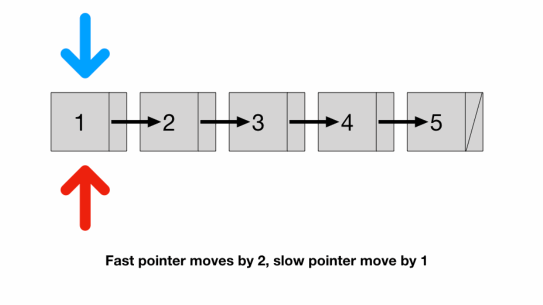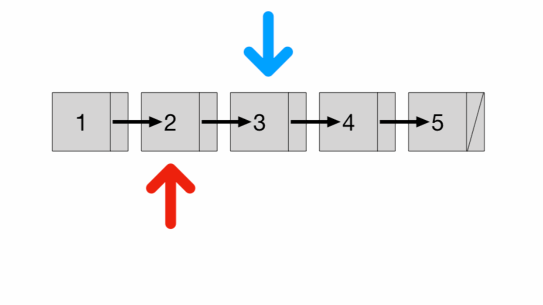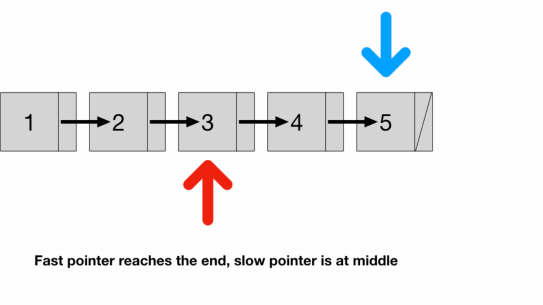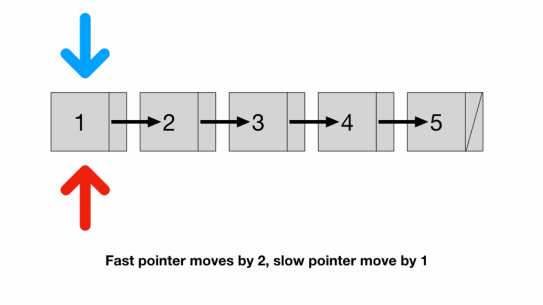
- Is there any way to traverse only once? We can use two pointers
- a fast pointer that moves 2 nodes at a time and
- a slow pointer that moves 1 node at a time
- Since the speed of the fast pointer is 2x of the slow pointer
- by the time the fast pointer reaches the end the slow pointer should be at exactly the middle of the list
- Time Complexity:
O(n)- Technically
O(n/2)but constants are cut out from the time complexity and so we are left with justO(n)
- Technically
- We have to check the existence of fast and fast.next in the while loop condition
- We have to check fast because if list length is odd (illustrated above)
- the fast pointer would reach the last node
- And if list length is even (illustrated below)
- the fast pointer would land on null (Node 6's next)