Insertion Sort
it is a simple sorting algorithm that works similar to the way you sort playing cards in your hands
- The array is virtually split into a sorted and an unsorted part
- Values from the unsorted part are picked and placed at the correct position in the sorted part
The running time of the insertionSort procedure depends on the set of input values
- it takes longer to sort thousands of numbers than to sort three numbers
- the running time of the algorithm increases with an increase in the amount of input data
- it is a common practice to represent the running time of a program as a function depending on the number of input elements
- For this, the concepts of "algorithm time" and "size of input data" need to be determined more precisely
The most adequate concept of input data size depends on the problem in question
- For each task considered below, the way of measuring the size of the input data will be indicated
- In the case of insertion sort, the number of input elements is considered as the size of the input data
The running time of an algorithm on a particular input is the number of primitive operations or "steps" executed
- It is convenient to define the notion of step so that it is as machine-independent as possible
To sort an array of size n in ascending order
- Iterate from arr[1] to arr[n] over the array
- Compare the current element (key) to its predecessor
- If the key element is smaller than its predecessor, compare it to the elements before
- Move the greater elements one position up to make space for the swapped element
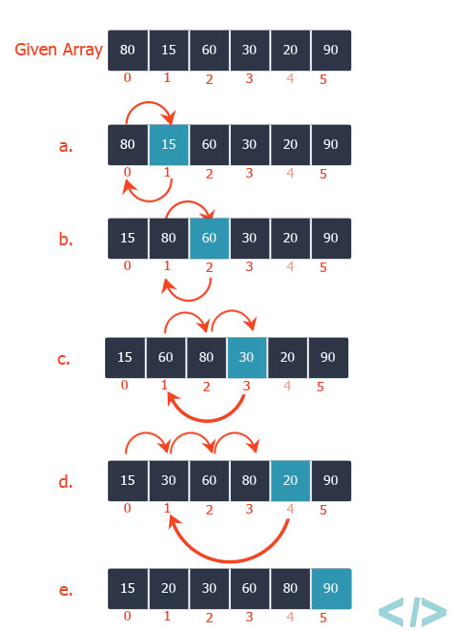
example
// prettier-ignore
function insertionSort(numbers: number[]) { // Cost | Repeats
for (let i = 1; i < numbers.length; i++) { // c[1] | n
const numberToSort = numbers[i]; // с[2] | n-1
let j = i - 1; // с[3] | n-1
while (j >= 0 && numbers[j] > numberToSort) { // c[4] | Sum(j=2, n) t[j]
numbers[j + 1] = numbers[j]; // c[5] | Sum(j=2, n) t[j-1]
j--; // c[6] | Sum(j=2, n) t[j-1]
}
numbers[j + 1] = numberToSort; // с[7] | n-1
}
}
const numbers = [1, 600, 199, 20, 7, 6, 8, 1300, 12, 601];
insertionSort(numbers);
console.log(numbers);