Merge Sort
The merge sort algorithm closely follows the divide-and-conquer paradigm
Dividethe n-element sequence to be sorted into two subsequences of n/2 elements eachConquer: Sort the two subsequences recursively using merge sortCombine: Merge the two sorted subsequences to produce the sorted answer
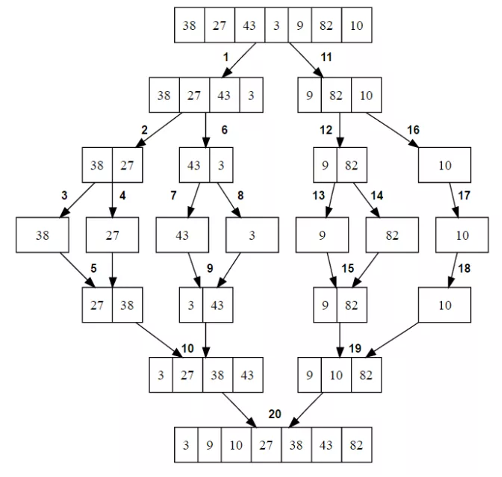
example
- We take half the length of the array and divide it into two parts
- And we call the merge function to the same sorting from the left and right sides
- The merge function itself compares and merges our sequences
- Although the code for merge sort works correctly when the number of elements is not even, our recurrence-based analysis is simplified if we assume that the original problem size is a power of 2
- Each divide step then yields two subsequences of size exactly n/2
- This assumption does not affect the order of growth of the solution to the recurrence
- We reason is to set up the recurrence for T(n), the worst-case running time of merge sort on n numbers
- Merge sort on just one element takes constant time
- When we have n > 1 elements, we break down the running time as follows:
Divide: The divide step just computes the middle of the subarray, which takes constant time- Thus, D(n) = Θ(1)
Conquer: We recursively solve two subproblems, each of size n/2, which contributes 2T(n/2) to the running timeCombine: We have already noted that the MERGE procedure on an n-element subarray takes time Θ(n), and so C(n) = Θ(n)
function merge(left: number[], right: number[]) {
const result = [];
const leftLength = left.length;
const rightLength = right.length;
let leftIndex = 0;
let rightIndex = 0;
while (leftIndex < leftLength && rightIndex < rightLength) {
if (left[leftIndex] < right[rightIndex]) {
result.push(left[leftIndex++]);
} else {
result.push(right[rightIndex++]);
}
}
while (leftIndex < leftLength) {
result.push(left[leftIndex++]);
}
while (rightIndex < rightLength) {
result.push(right[rightIndex++]);
}
return result;
}
function mergeSort(numbers: number[]): number[] {
const length = numbers.length;
const mid = Math.floor(length * 0.5);
const left = numbers.slice(0, mid);
const right = numbers.slice(mid, length);
if (length === 1) {
return numbers;
}
return merge(mergeSort(left), mergeSort(right));
}
console.log(mergeSort([1, 600, 199, 20, 7, 6, 8, 1300, 12, 601]));- We take half the length of the array and divide it into two parts